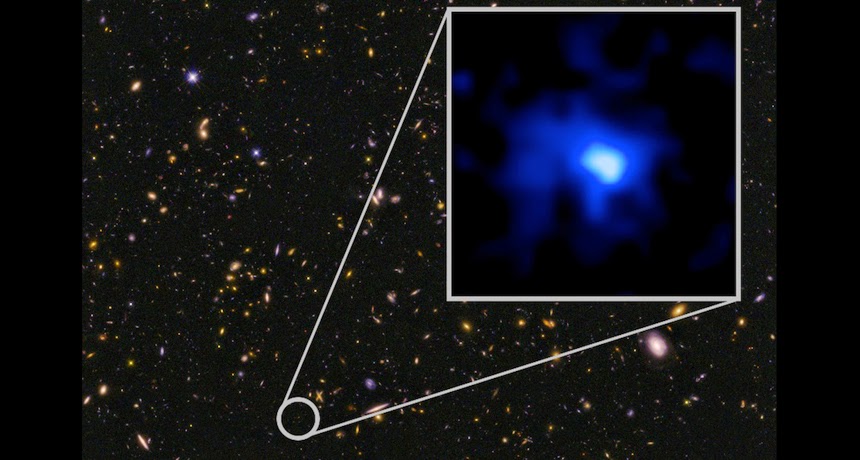
A new distant galaxy, containing approximately 8 billion stars, has been discovered by astronomers.1 What makes this galaxy, named EGS-zs8-1, unique is that it is 13 billion light years away from earth making it the most distant galaxy that has ever been seen. The light that is now reaching the Hubble Space Telescope left that galaxy 13 billion years ago when the universe was a mere 650 million years old.2 Presently, the universe is estimated to be roughly 13.6 to 13.9 billion years old.
What are the philosophical and theological implications of seeing a galaxy that is 13 billion light years away? Those who follow the Christian faith have long argued about how long the universe, earth, and humans have been around. Some take a hyper-literal perspective on the words of the Bible and believe that the universe cannot be more than 6000 years old. Some suggest that the universe only looks old because God made it mature.3 They suggest that God formed the universe with light from distant galaxies already partway here.
It is possible to think that way, but I would suggest that a much more straight-forward way of dealing with such discoveries is to agree that God has created a scientifically discernible universe in which, if something looks 13 billion years old, it is likely 13 billion years old (barring some sort of unnoticed calculation error). Of course, this way of thinking also assumes that God took a progressive approach to creation and took billions of years to bring us to where we are today. This kind of thinking will not do if one wants to maintain that the universe went from the chaos of nothing to a fully formed universe with plants, animals, and humans in six 24 hour periods of time. There are many further ramifications of thinking of the universe as very old, but we must be rigorous and not fear the implications of examining the evidence and drawing conclusions. A God who has created a universe that includes galaxies filled with 8 billion stars, 13 billion light years away, is capable of communicating with humans to explain the universe and his own nature.
1 https://www.sciencenews.org/blog/science-ticker/amorphous-space-blob-takes-title-most-distant-galaxy?tgt=nr
2 A Spectroscopic Redshift Measurement for a Luminous Lyman Break Galaxy at z = 7.730 Using
Keck/MOSFIRE; P. A. Oesch and P. G. van Dokkum and G. D. Illingworth and R. J. Bouwens and I. Momcheva and B. Holden and G. W. Roberts-Borsani and R. Smit and M. Franx and I. Labbé and V. González and D. Magee; 2015; p. 30; The Astrophysical Journal Letters; Volume 804; Issue 2
3 http://www.icr.org/article/5669/